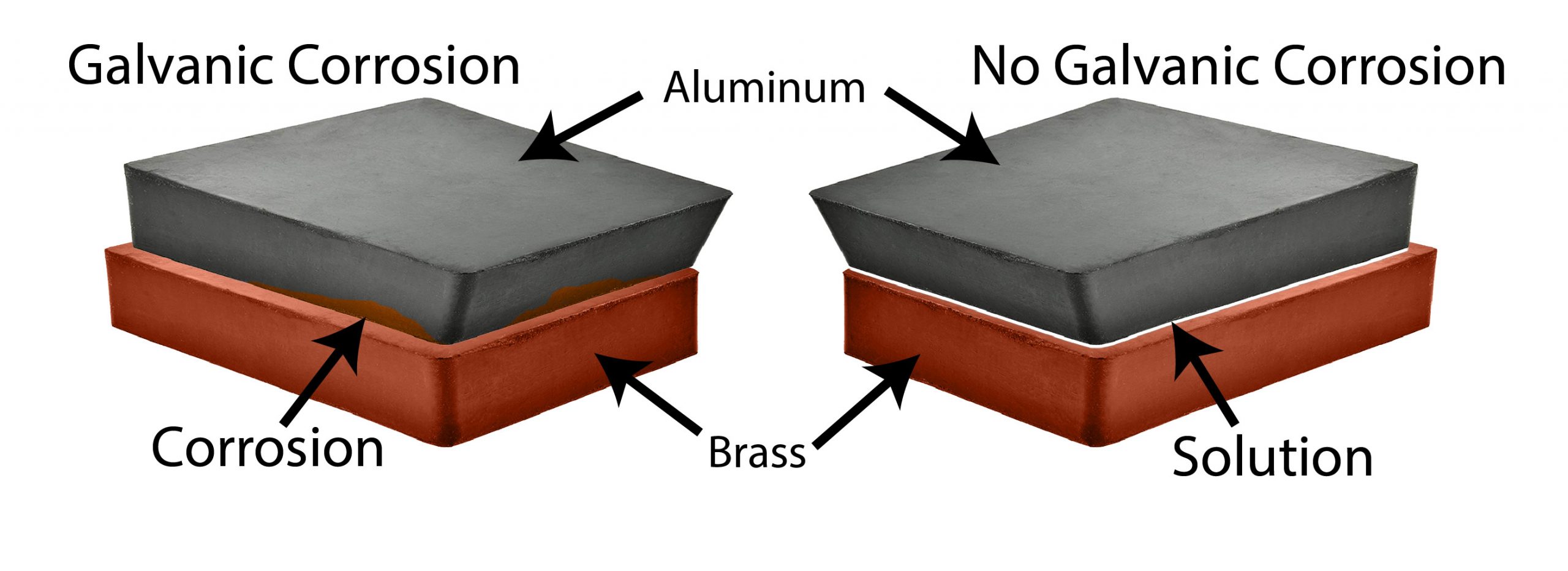
What is galvanic corrosion?
When two dissimilar metals are brought into electrical contact, Galvanic Corrosion occurs. The electrical contact of these two metals changes their corrosion rates. One of the dissimilar metals corrodes faster than it normally would by itself, while the other dissimilar metal corrodes slower than it would by itself.
Different weathering environments, such as water, heat, and humidity, can cause galvanic corrosion. Other factors, such as the way the components are assembled, the metals involved, and more, can also play into the effects.
A great example of Galvanic Corrosion is the Statue of Liberty. In the 1980s a regular maintenance check revealed that corrosion had accrued between the copper outer skin and the wrought iron support structure.
Corrosion can also occur with dissimilar metals on a vehicle. When you have a spare tire that is located under a vehicle, the spare tire is mounted in a heat resistant shield. That shield is then mounted to the frame under a vehicle. The heat resistant shield and frame of the vehicle are two different metals. The mount where these two are mounted together can develop galvanic corrosion. There are solutions to prevent this from occurring.
How To Prevent Galvanic Corrosion
By following these strategies, you can help prevent galvanic corrosion, ensuring your equipment and labels remain in excellent condition over time:
- Choose Compatible Metals: Select metals close to each other on the galvanic series to minimize this risk. For example, using stainless steel fasteners with aluminum components could reduce the chance of corrosion. As your labeling partner, we recommend considering compatible materials when selecting label hardware and attachments.
- Apply Protective Coatings: Coatings act as a barrier to prevent contact between different metals. Protective coatings, such as epoxy or anodizing, can shield your label and equipment from electrolytes, reducing the likelihood of corrosion. Consider working with a supplier who offers labels with specialized coatings designed for high-corrosion environments.
- Use Insulating Materials: Providing an insulating layer between dissimilar metals effectively breaks the conductive path that leads to corrosion. Non-conductive materials, like plastic or rubber, can be used as gaskets, washers, or spacers to keep metals from directly touching. This simple step can drastically improve the longevity of your labels and equipment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which metal combinations are most susceptible to galvanic corrosion?
Metals that are far apart on the galvanic series are the most vulnerable when paired together. Common high-risk combinations include aluminum with stainless steel, carbon steel with copper, and zinc with brass. The greater the potential difference between the two metals, the higher the risk of accelerated corrosion under conductive environmental conditions.
What environments increase the risk of galvanic corrosion?
Galvanic corrosion is more likely to occur in environments where electrolytes are present. This includes marine and coastal settings, outdoor industrial applications, chemical processing facilities, and areas exposed to road salt or frequent washdowns. High humidity, condensation, and temperature fluctuations can also increase the likelihood of corrosion over time.
Are coatings effective at preventing galvanic corrosion?
Yes, coatings can be highly effective when properly specified and applied. Protective coatings act as a barrier between dissimilar metals and the surrounding environment, reducing electrical contact and limiting exposure to electrolytes. However, coating integrity is critical. Scratches, wear, or incomplete coverage can create localized corrosion points that accelerate damage rather than prevent it.
Get Answers To Your Galvanic Corrosion Questions
Whitlam’s engineering team has developed various solutions to help eliminate galvanic corrosion. With our In-House lab and R&D team we can test products and come up with the best solution for your products need. At Whitlam our goal is to make the tough stuff easy. Let us help you; contact us today for more information.